BIOMÉRIEUX EPISEQ®
Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) Data Analysis Platform
Provides easy-to-use applications for clinical microbiologists: clinical pathogen outbreak management, microbiome profiling, and SARS-CoV-2 genomics variants identification.
Disclaimer: Product availability varies by country. Please consult your local bioMérieux representative for product availability in your country.
Not for diagnostic use.

- Overview
- EPISEQ CS
- EPISEQ 16S
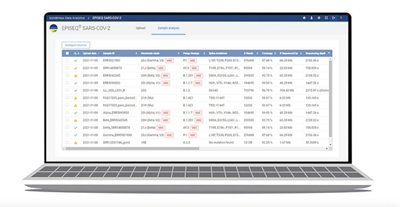
- EPISEQ SARS-COV-2
- Resources
Overview
Actionable Answers, Fast.
BIOMÉRIEUX EPISEQ® is an innovative next generation sequencing (NGS) service that combines a state-of-the-art bioinformatics pipeline with meaningful microbiological data to answer meaningful microbiological questions.
The process starts by simply importing raw data directly from NGS instruments. With a fast and intuitive workflow, in just a few clicks, BIOMÉRIEUX EPISEQ® will convert that data into actionable results.
Discover our three software applications:
EPISEQ® CS
For Clinical Pathogens Outbreak Monitoring
EPISEQ® CS performs bacterial typing based on Whole Genome Sequencing data and Mutli Resistant Bacteria characterization. It helps to confirms HAI outbreaks early and accurately. It allows to track level of resistance genes within the hospital. It reports decisive data to further investigate a potential outbreak or cluster, thus triggering infection prevention and control (IPC) protocols at an early stage to limit the spread of the outbreak.
Ease of Use
- A one-click solution for cluster determination and outbreak management
- Direct import of Illumina WGS data (FASTQ or FASTA)
- Comprehensive sample characterization and genotyping info
- Phylogenetic visualization tools (dendrogram and minimum spanning tree)
- PDF-downloadable reports
Microbiology Expertise / Antimicrobial Resistance
- Covers the vast majority of Hospital Acquired Infection (HAI)-related organisms
- Built-in wgMLST scheme for each organism
- Display of conventional typing data where available (MLST, spa type, serotype, pathotype)
- More than 4,000 resistance genes embedded with associated phenotypes
- Detects resistance genes carried out by plasmids
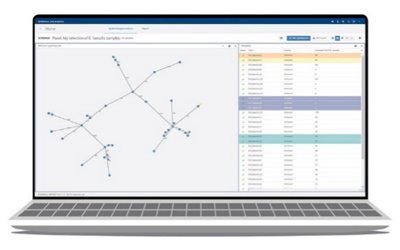
EPISEQ® CS
Fast and Intuitive Workflow
Extensive List of Bacterial Species
bioMérieux has long been a partner to healthcare professionals in the battle against AMR and Healthcare Associated Infections in particular - offering innovative culture media, ID/AST reagents and instruments for rapid, reliable microbiology testing along with environmental control solutions and educational support.
With EPISEQ® CS we are now able to offer you an application that will help you manage HAI in your facilities. The online tool puts NGS technology, along with one of the world's most extensive databases of bacterial strains at your disposal. You will gain critical information to track, help prevent, contain, and stop the spread of infectious diseases and HAI.
bioMérieux has identified 14 bacterial species that cover most HAI-related organisms:
- Acinetobacter baumannii
- Clostridioides difficile
- Enterococcus faecalis
- Acinetobacter baumannii
- Klebsiella oxytoca
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Burkholderia cepacia complex
- Escherichia coli / Shigella
- Klebsiella pneumoniae
- Enterococcus faecium
- Citrobacter freundii
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Klebsiella aerogenes
- Serratia marcescens
EPISEQ® 16S
For Microbiome Profiling Studies
EPISEQ® 16S helps to investigate the role of MICROBIOME on patient's health. It covers the full diversity of bacteria and archaea with relative abondance and richness. This solution supports users to discover predictive biomarkers within microbiota.
Ease of Use
- An intuitive and easy solution to identify patterns in microbiota and their associations with clinical outomes or the impact of antibiotic treatment on a given microbiota
- Directly import Illumina 16S amplicon raw data (FASTQ)
- Extensive set of visualization tools to explore data
- Built-in statistics that allow you to trust your results
- Time-interaction analysis
- Customized report that displays what is important for you to know
Microbiology Expertise / Antimicrobial Resistance
- Covers the full diversity of bacteria and archaea (SILVA 138, 2019-12-16)
- Display of relative abundance
- Display of alpha and beta diversity
- Clustering of data
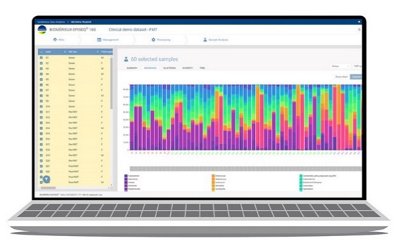
EPISEQ® 16S
Fast and Intuitive Workflow
EPISEQ® SARS-COV-2
For SARS-CoV-2 Variant Identification
EPISEQ® SARS-COV-2 allows to identify SARS -COV-2 genomic variants without bioinformatics skills. Users can perform on routine base variant analysis and download the required files to submit to public health authority for compliance (FastA file, variant call and BAM files).
Ease of Use
- A one-click solution to identify SARS-CoV-2 variants starting from raw sequencing data
- Direct import of FASTQ files:
- Illumina (paired-end or single-end)
- Thermo Fisher Ion Torrent™
- Oxford Nanopore Technologies
- A comprehensive report per sample is available for download
Microbiology Expertise / Antimicrobial Resistance
- Display of quality control information
- Variant identification based on Nextstrain¹ and Pango² nomenclature
- Weekly updates of the Pango and Nextstrain nomenclatures
- List of mutations detected in all genes of the SARS-CoV-2 genome, including the spike gene
- Identification of Variant of Concern based on WHO³ and CDC⁴
- Alignment of reads against the reference available for download in BAM format
- Genome assembly available for download in FASTA format