TTV R-GENE®
Guiding Transplant Risk Management
Disclaimer: Product availability varies by country. Please consult your local bioMérieux representative for product availability in your country.
- TTV R-GENE
- Overview
- Assay
- Resources
Overview
Torque Teno Virus (TTV): A Surrogate Marker of Immune Function
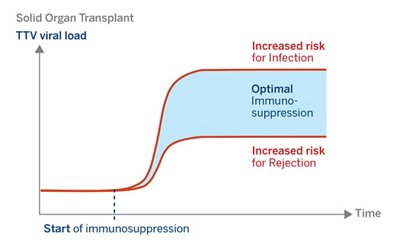
Graft rejection due to inadequate immunosuppression is the leading cause for chronic graft dysfunction and infectious disease due to reduced immune function is a major cause of death. Optimization of immunosuppressive drugs is a crucial step to minimize the risk of infection and rejection and thereby prolonging patient and graft survival.
The Torque Teno Virus (TTV) is a non-pathogenic virus carried by nearly everyone and interestingly, research has demonstrated TTV peripheral blood copy number is associated with the grade of the immunosuppression of the host1,2,3. If the immune system is strong, the TT virus load is low; this indicates a risk for graft rejection4,5. If the immune system is weak, the TT virus load is high; this indicates a risk of opportunistic infections6,7,8.
European Project on Kidney Transplant
A EU funded project - TTV GUIDE TX - aims to demonstrate the safety and preliminary efficacy of TTV-guided dosing of immunosuppressive drugs in kidney transplant recipients. TTV allows for a comprehensive and personalized assessment of the function of the immune system. For the first time, this novel and original approach will be tested in an interventional, randomized, and controlled clinical trial including hundreds of kidney transplant recipients from all over Europe.
Coordinated by the Medical University of Vienna (Austria), the TTV GUIDE TX brings together 19 partners from 7 EU countries, including kidney transplant physicians, clinical virologists, project and clinical trial managers, ethicists and bioMérieux, to run a clinical trial with almost 300 patients.
The TTV GUIDE TX project will work closely together with The European Kidney Patients’ Federation (EKPF), the European umbrella organization for 23 national kidney patients’ associations. Once established in routine clinical care, TT virus guidance might reduce thousands of infections and kidney transplant rejections each year.
In the future the TT virus might not only help kidney transplant recipients but also patients with liver, heart, and lung transplantation and guide therapy in autoimmune, infectious, and oncologic diseases.
Find out more about the project at: https://www.ttv-guide.eu/
Please go to: https://vimeo.com/545093421 to see the project video.
List of partners:

TTV R-GENE® Kit: A Promising Biomarker for Tailored Transplant Patients Management
The TTV R‑GENE® kit, using the real‑time PCR technology after extraction of the viral DNA, enables the detection and quantification of the genome of TTV in whole blood and plasma samples.
Combined with other biological investigation methods (medical imaging, white blood cell count, lymphocyte phenotyping, etc.), the results obtained with the TTV R‑GENE® kit enable TTV viral load monitoring and are an aid to assess the immune function: TTV viral load monitoring can be used to evaluate the immune status of adult transplant patients.
This kit is intended for in vitro diagnostic use only, in clinical laboratories by laboratory health professionals.
Guiding Transplant Risk Management
Torque Teno Virus
ARGENE® Expertise
- Simplicity: complete kits, ready-to-use reagents, same pipetting procedure
- Seamless Integration: validated for use on multi-specimens, multi-extraction, and multi-amplification platforms
- Lab Efficiency: common internal control, harmonized extraction and amplification protocols, multiple targeted detection from one extracted sample
References
1. Fernández-Ruiz M, et al. Monitoring of alphatorquevirus DNA levels for the prediction of immunosuppressionrelated complications after kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2019 Apr;19(4):1139-1149.
2. Rezahosseini O et al. Torque-Teno virus viral load as a potential endogenous marker of immune function in solid organ transplantation. Transplant Rev. 2019 Jul;33(3):137-144.
3. De Vlaminck, I. et al. Temporal Response of the Human Virome to Immunosuppression and Antiviral Therapy. Cell 155, 1178–1187 (2013).
4. Rezahosseini O, Drabe CH, Sørensen SS, Rasmussen A, Perch M, Ostrowski SR, Nielsen SD. Torque-Teno virus viral load as a potential endogenous marker of immune function in solid organ transplantation. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2019 Jul;33(3):137-144. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30981537/
5. Strassl R, Doberer K, Rasoul-Rockenschaub S, Herkner H, Görzer I, Kläger JP, Schmidt R, Haslacher H, Schiemann M, Eskandary FA, Kikić Ž, Reindl-Schwaighofer R, Puchhammer-Stöckl E, Böhmig GA, Bond G. Torque Teno Virus for Risk Stratification of Acute Biopsy-Proven Alloreactivity in Kidney Transplant Recipients. J Infect Dis. 2019 May 24;219(12):1934-1939. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30668796/
6. Gore EJ, Gomes-Neto AW, Wang L, Bakker SJL, Niesters HGM, de Joode AAE, Verschuuren EAM, Westra J, Leer-Buter CV. Torquetenovirus Serum Load and Long-Term Outcomes in Renal Transplant Recipients. J Clin Med. 2020 Feb 6;9(2):440. doi: 10.3390/jcm9020440.
7. Fernández-Ruiz M, Albert E, Giménez E, Ruiz-Merlo T, Parra P, López-Medrano F, San Juan R, Polanco N, Andrés A, Navarro D, Aguado JM. Monitoring of alphatorquevirus DNA levels for the prediction of immunosuppression related
8. Strassl R, Schiemann M, Doberer K, Görzer I, Puchhammer-Stöckl E, Eskandary F, Kikic Ž, Gualdoni GA, Vossen MG, Rasoul-Rockenschaub S, Herkner H, Böhmig GA, Bond G. Quantification of Torque Teno Virus Viremia as a Prospective Biomarker for Infectious Disease in Kidney Allograft Recipients. J Infect Dis. 2018 Sep 8;218(8):1191-1199
Assay
| Kit Designation | Reference | Type Of Kit | Number Of Tests | Regulatory Status* |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TTV R-GENE® | 423414 | Real-time detection and quantification kit | 90 | For In vitro diagnostic use (IVDR) |
| TTV R-GENE® (423414) | |
|---|---|
| Principle of the test | Genomic detection and quantification of TTV |
| Ordering information | Reference: 423414 Designation: TTV R-GENE® Real-Time Detection and Quantification kit |
| Technology | Real-Time PCR / 5‘ nuclease Taqman technology |
| PCR design & Gene target | TTV 5'-UTR region |
| Kit content | All included (Amplification premix, Internal control, Negative control, Quantification standards) |
| Controls included | Extraction + Inhibition control, Sensitivity control, Negative control |
| Specimen |
|
| Dynamic Range of Quantification | 250 copies/mL and 1.0E+09 copies/mL |
| Results within | 75 minutes (extraction step not included) |
| Reporting unit | Copies/mL |
| Validated Extraction platform |
|
| Validated Amplification platform |
|
| Number of tests | 90 tests |
| Storage conditions | -15°C/-31°C |
| Status | For in vitro diagnostic use (IVDR*) |
*IVDR: CE marked under EU regulation 2017/746
Resources
%20Selection%20Of%20Publications%20thumbnail?qlt=85&ts=1706264179814&dpr=off)
