VIDAS® B·R·A·H·M·S PCT™
Improve Patient Outcomes and Optimize Patient Management
Detects procalcitonin, a biomarker that aids in the risk assessment for progression to severe sepsis and septic shock. PCT also aids in decision making on antibiotic therapy for patients with lower respiratory tract infections (LRTI).
Disclaimer: Product availability varies by country. Please consult your local bioMérieux representative for product availability in your country.

- VIDAS BRAHMS PCT
- Overview
- Assay
- Resources
Overview
In recent years, procalcitonin (PCT) has become an increasingly used blood biomarker for improved management of patients with systemic infections and sepsis. It is an important biomarker in assessing disease severity and prognosis, and also guiding clinical decisions on antibiotic therapy.
A growing concern for Health Care Systems worldwide is to reduce the unnecessary and prolonged use of antibiotics. Diagnostic tools and biomarkers are urgently needed which allow better assessment of a patient’s risk of having an infection, and their response to antibiotic therapy.
One such blood biomarker is procalcitonin (PCT), which is increasingly used in clinical practice for improved patient management. During clinically relevant bacterial infections, PCT blood levels rise within 4-6 hours, and these levels mirror the kinetics of the infection. PCT levels drop by about 50% daily when infection is controlled and responds adequately to antibiotics.
Procalcitonin is a host-response biomarker that has shown clinical value for assessing the likelihood of bacterial infections and guiding antibiotic treatment.1
PCT in Sepsis
In sepsis, PCT levels are elevated several-fold in nearly all tissues. In cases of sepsis or septic shock in adults where the ideal duration of therapy remains uncertain, the 2021 Surviving Sepsis Guidelines recommend combining procalcitonin assessment with clinical evaluation for making the decision to discontinue antimicrobial treatment, as opposed to relying solely on clinical evaluation.2
PCT is the most useful for multiple measurements, in decision making on antibiotic discontinuation for patients with suspected or confirmed sepsis.
Note 1: cut-off range depends on clinical condition, co-morbidities, severity signs, site of infection etc.
Note 2: PCT can not identify the microorganism (and should therefore be used together with microbiology testing), and PCT shall always be used in conjunction with clinical evaluation.
VIDAS® B•R•A•H•M•S PCT™ INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS
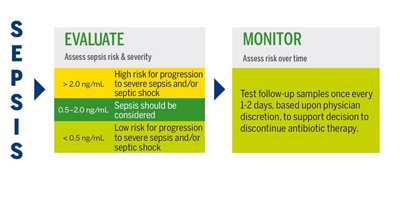
Antibiotic therapy should be considered regardless of PCT result if the patient is clinically unstable, is at high risk for adverse outcome, has strong evidence of bacterial pathogen, or the clinical context indicates antibiotic therapy is warranted.
PCT in Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
Research indicates that 30% of 60% of antibiotics prescribed in ICUs are unnecessary, inappropriate, or suboptimal.
In primary care, as many as 75% of patients with LRTI are treated with antibiotics, despite the predominantly viral origin of their infection.
Lower respiratory tract infections are amongst the main causes for hospital/intensive care unit admissions and antimicrobial prescriptions. Procalcitonin-guided antibiotic administration has proven its efficacy in reducing unnecessary antibiotic use in lower respiratory tract infections without excess in mortality, hospital length of stay, or disease relapse.3
VIDAS® B•R•A•H•M•S PCT™ INTERPRETATION OF RESULTS
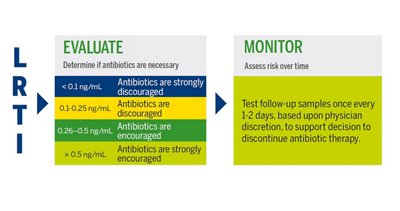
Antibiotic therapy should be considered regardless of PCT result if the patient is clinically unstable, is at high risk for adverse outcome, has strong evidence of bacterial pathogen, or the clinical context indicates antibiotic therapy is warranted.
VIDAS® Solutions
- Reliable and easy-to-use instruments with random access and small footprint.
- Well adapted to rapid response laboratories.
- Factory-calibrated, single-dose tests which reduce the need for additional controls.
- Short time to result.
- Reagents can be used immediately after removal from the refrigerator.
References
1. Schuetz, P. (2023). How to best use procalcitonin to diagnose infections and manage antibiotic treatment. Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM), 61(5), 822-828. https://doi.org/10.1515/cclm-2022-1072
2. Surviving Sepsis Campaign Guidelines: International Guidelines for Management of Sepsis and Septic Shock 2021. Critical Care Medicine 49(11):p e1063-e1143, November 2021. doi:10.1097/CCM.0000000000005337
3. Saura O, Luyt CE. Procalcitonin as a biomarker to guide treatments for patients with lower respiratory tract infections. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2023;17(8):651-661. doi:10.1080/17476348.2023.2251394
Assay
Technical Specifications
| Assay | Reference | Tests per Kit | Code | Time to Result | Measuring Range or Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VIDAS® B·R·A·H·M·S PCT™ | 30450 30450-30 | 60 tests 30 tests | PCT | 20 minutes | 0.05 - 200 ng/mL |
BECAUSE IT MAKES SENSE ON VIDAS®

Resources